
icRamp Devlog #20 — Pay with Crypto (Settlement & Verification)
In Devlog #19 — Pay with Crypto (Frontend), I wired the profile and Create Order UX so offramper/onramper can attach Crypto providers (EVM, Solana, ICP), and use them as a payment method when locking an order.
This post covers the missing half: settling a Locked order with crypto and having the backend verify the payment:
- Frontend: “Pay with Crypto” button on Locked orders
- Chain-aware hooks (
useOrderEvm,useOrderSolana,useOrderIcp) - Provider-asset-aware amount calculation in token units
- Backend: new pay-with-crypto verification path, especially for EVM
It turns the previous “UX shell” into a full end-to-end P2P bridge between chains.
Locked orders now have a “Pay with Crypto” button
Once an onramper commits to a provider and the order transitions from Created → Locked,
we now show a pay-with-crypto button when the committed provider is of type Crypto.
Visually it looks like this:
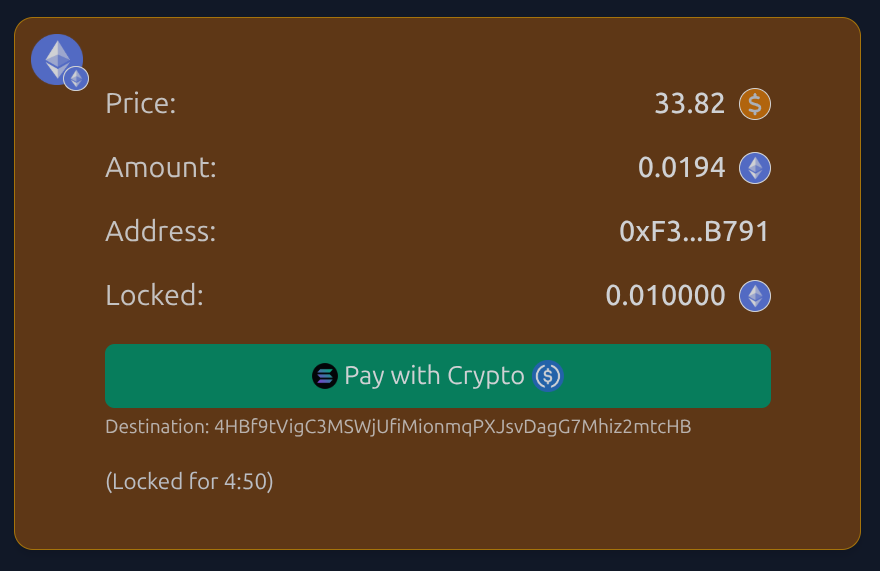
Key points:
- The pill on the left is not the order asset, it’s the onramper’s crypto provider:
- chain (EVM / Solana / ICP),
- the actual network (e.g. Sepolia),
- the token logo (e.g. USDC).
- The button text reads e.g.
Pay with Crypto (Solana)orPay with Crypto (Sepolia, chain 11155111)based purely on the provider asset, not the locked order’scrypto.asset.
This uses the same helpers as the Created view:
const provider = orderState.Locked.onramper.provider;
const providerType = paymentProviderTypeToString(
providerToProviderType(provider),
);
const { chain, evmNetwork, token } = describeCryptoProvider(provider);
<span className="inline-flex items-center gap-1 px-3 py-1 rounded-full border text-sm bg-gray-700/40 border-gray-500/60 text-gray-200 cursor-default">
<ProviderIcon
type={providerType}
className="h-4 w-auto rounded-md"
crypto={chain ?? undefined}
evmChain={evmNetwork?.id ?? undefined}
/>
<span>{providerType}</span>
{token?.logo && (
<img src={token.logo} alt={token.logo} className="h-5 w-auto rounded-md" />
)}
</span>So the Locked view is consistent with the create-order “Payment Methods” UI: same describeCryptoProvider, same ProviderIcon, same mental model.
The onClick just calls a new hook function:
<button
onClick={handleCryptoPay}
disabled={!isPayable || isLoading || orderState.Locked.payment_done}
>
Pay with Crypto {/* + chain label */}
</button>The rest of the story is inside handleCryptoPay.
handleCryptoPay: from Locked order to on-chain payment
The core of the frontend logic lives in the order hook:
// in useOrderLogic.ts
const handleCryptoPay = async () => {
if (!sessionToken)
throw new Error('Please authenticate to get a token session');
if (!('Locked' in orderState) || !orderId) return;
if (!user || !('Onramper' in user.user_type)) return;
const locked = orderState.Locked;
const provider = locked.onramper.provider;
if (!('Crypto' in provider)) return;
// 1) Resolve provider chain + token (e.g. USDC on Sepolia or USDC on Solana)
const { chain, evmNetwork, token: providerToken } =
describeCryptoProvider(provider);
if (!chain || !providerToken) {
throw new Error('Unable to resolve crypto provider token');
}
// 2) Convert fiat price+fee → token amount using providerToken.decimals
const amountFiatCents =
BigInt(locked.price) + BigInt(locked.offramper_fee); // price + offramper fee
const decimalsBig = BigInt(providerToken.decimals ?? 6);
const amountUnits =
(amountFiatCents * (10n ** decimalsBig)) / 100n;
// 3) Find Offramper's matching crypto provider (same asset)
const offramperCryptoProvider = locked.base.offramper_providers.find((p) => {
if (!('Crypto' in p)) return false;
return sameCryptoAsset(provider.Crypto.asset, p.Crypto.asset);
});
if (!offramperCryptoProvider || !('Crypto' in offramperCryptoProvider)) {
throw new Error('Offramper has no matching crypto provider for this asset/chain');
}
const dstAddress = offramperCryptoProvider.Crypto.address.address;
setIsLoading(true);
setTxHash(null);
setMessage(null);
setLoadingMessage('Submitting crypto payment from your wallet');
try {
let depositInput: [] | [DepositInput] = [];
let paymentTxId = '';
if (chain === 'EVM') {
const evmAsset = 'EVM' in provider.Crypto.asset ? provider.Crypto.asset.EVM : undefined;
const chainId =
evmAsset?.chain_id != null ? Number(evmAsset.chain_id) : evmNetwork?.id;
if (!chainId) throw new Error('Missing EVM chain id for crypto provider');
const { depositInput: evmDep, txHash } = await makeEvmCryptoPayment(
chainId,
providerToken,
amountUnits,
dstAddress,
);
depositInput = evmDep;
paymentTxId = txHash;
} else if (chain === 'Solana') {
const { depositInput: solDep, txSig } =
await makeSolanaCryptoPayment(amountUnits, providerToken, dstAddress);
await waitForSolanaConfirmation(txSig, { timeoutMs: 90_000 });
depositInput = solDep;
paymentTxId = txSig;
} else if (chain === 'ICP') {
if (!icpAgent) throw new Error('ICP Agent not found');
await makeIcpPayment(icpAgent, providerToken, amountUnits, dstAddress);
// No on-chain verification for ICP today
depositInput = [];
paymentTxId = '';
} else {
throw new Error('Unsupported crypto provider chain');
}
// 4) Ask the backend to verify the tx and release funds
const response = await backend.verify_transaction(
orderId,
[sessionToken],
paymentTxId,
depositInput,
);
if ('Ok' in response) {
// same post-verify routing as PayPal/Stripe
if ('EVM' in orderBlockchainAsset!) {
setTxHash(response.Ok);
await pollTransactionLog(orderId, user.id);
} else if ('Bitcoin' in orderBlockchainAsset!) {
setTxHash(response.Ok);
setLoadingMessage(
'Bitcoin transaction is being processed. This may take some time to confirm.',
);
await waitForProcessingAndRoute(orderId);
} else if ('Solana' in orderBlockchainAsset!) {
setTxHash(response.Ok);
setLoadingMessage('Confirming Solana transaction');
await waitForProcessingAndRoute(orderId);
} else {
await waitForProcessingAndRoute(orderId);
}
} else {
const errorMessage = rampErrorToString(response.Err);
setMessage(errorMessage);
}
} catch (err: any) {
setMessage(err?.message ?? String(err));
} finally {
setIsLoading(false);
}
};Highlights:
- Provider-centric: the branch (
EVMvsSolanavsICP) is decided bylocked.onramper.provider.Crypto.asset– not by the order’scrypto.asset. - The amount is
(price + offramper_fee)in fiat, converted to smallest token units using the provider tokendecimals. This matches exactly what we charge via Stripe/PayPal. - We always send to the offramper’s crypto provider address that shares the same asset (
sameCryptoAsset()between onramper/offramper providers).
The hooks we call (makeEvmCryptoPayment, makeSolanaCryptoPayment, makeIcpPayment) are thin wrappers around chain-specific payment helpers.
Chain-specific payment helpers
Solana: makeSolanaCryptoPayment
On the Solana side we already had makeSolanaDeposit, which sent tokens to the canister vault when creating an order.
For pay-with-crypto we added a sibling that pays any destination address:
// in useOrderSolana.ts
const makeSolanaCryptoPayment = async (
amountUnits: bigint,
token: TokenOption,
destinationAddress: string,
) => {
if (!publicKey) throw new Error('Please connect your Solana wallet');
const dstPk = new PublicKey(destinationAddress);
const tx = new Transaction();
let mintOpt: [] | [string] = [];
if (token.isNative) {
const lamports = Number(amountUnits);
if (!Number.isSafeInteger(lamports)) throw new Error('Amount too large');
tx.add(
SystemProgram.transfer({
fromPubkey: publicKey,
toPubkey: dstPk,
lamports,
}),
);
} else {
const mintStr = token.address;
mintOpt = [mintStr];
const programId = await getMintProgramId(mintStr);
const mint = new PublicKey(mintStr);
const fromAta = await getAssociatedTokenAddress(
mint,
publicKey,
false,
programId,
);
const toAta = await getAssociatedTokenAddress(
mint,
dstPk,
true,
programId,
);
// auto-create destination ATA if needed
const ataInfo = await connection.getAccountInfo(toAta, {
commitment: 'confirmed',
});
if (!ataInfo) {
tx.add(
createAssociatedTokenAccountInstruction(
publicKey,
toAta,
dstPk,
mint,
programId,
),
);
}
tx.add(
createTransferCheckedInstruction(
fromAta,
mint,
toAta,
publicKey,
amountUnits,
token.decimals,
[],
programId,
),
);
}
const { blockhash } = await connection.getLatestBlockhash('processed');
tx.recentBlockhash = blockhash;
tx.feePayer = publicKey;
const sig = await sendTransaction(tx, connection, {
skipPreflight: false,
maxRetries: 0,
});
const depositInput: [DepositInput] = [
{
Solana: {
signature: sig,
mint: mintOpt,
},
},
];
return { depositInput, txSig: sig };
};We still reuse the existing waitForSolanaConfirmation loop to get a finalized signature before calling verify_transaction.
EVM: sendEvmPayment + makeEvmCryptoPayment
For EVM, we don’t hit the vault contract at all – we just perform a plain transfer:
// in evm.ts
export const sendEvmPayment = async (
chainId: number,
selectedToken: TokenOption,
cryptoAmount: bigint,
toAddress: string,
) => {
if (!window.ethereum)
throw new Error('No crypto wallet found. Please install it.');
const provider = new ethers.BrowserProvider(window.ethereum);
await provider.send('eth_requestAccounts', []);
// enforce the correct chain in MetaMask
const network = await provider.getNetwork();
const walletChainId = Number(network.chainId);
if (walletChainId !== chainId) {
throw new Error(
`Wrong EVM network in wallet. Expected chain id ${chainId}, but wallet is on ${walletChainId}.`,
);
}
const signer = await provider.getSigner();
// normalise destination address (avoid ENS issues)
const checksumTo = ethers.getAddress(toAddress);
let txResponse;
if (selectedToken.isNative) {
const gasEstimate = await signer.estimateGas({
to: checksumTo,
value: cryptoAmount,
});
txResponse = await signer.sendTransaction({
to: checksumTo,
value: cryptoAmount,
gasLimit: gasEstimate,
});
} else if (selectedToken.address !== '') {
const tokenContract = new ethers.Contract(
selectedToken.address,
['function transfer(address to, uint256 amount) external returns (bool)'],
signer,
);
const gasEstimate = await tokenContract.transfer.estimateGas(
checksumTo,
cryptoAmount,
);
txResponse = await tokenContract.transfer(checksumTo, cryptoAmount, {
gasLimit: gasEstimate,
});
} else {
throw new Error('No token selected');
}
const receipt = await txResponse.wait();
if (receipt.status !== 1) {
throw new Error('Transaction failed on-chain.');
}
return receipt;
};useOrderEvm then wraps it into a DepositInput:
const makeEvmCryptoPayment = async (
chainId: number,
token: TokenOption,
amount: bigint,
toAddress: string,
) => {
const receipt = await sendEvmPayment(chainId, token, amount, toAddress);
const depositInput: [DepositInput] = [
{
Evm: {
estimated_gas_lock: 0n,
estimated_gas_withdraw: 0n,
tx_hash: receipt.hash,
},
},
];
return { depositInput, txHash: receipt.hash };
};So the backend still receives a familiar DepositInput::Evm value – just with gas fields set to 0.
ICP: trusted-agent path
For ICP we cannot verify txs from inside the canister (no generic EVM-style view into ICP ledgers), so the pay-with-crypto path is more conservative:
- We check that the ICP token is supported.
- We rely on the agent (frontend) to execute the transaction correctly.
- On the backend we essentially just treat it as “paid” once the agent reports success.
The hook reflects that:
const makeIcpPayment = async (
agent: HttpAgent,
token: TokenOption,
amount: bigint,
destination: string,
) => {
const ledger = Principal.fromText(token.address);
const fees = await fetchIcpTransactionFee(ledger);
const recipient = Principal.fromText(destination);
const result = await transferICPTokens(
agent,
ledger,
recipient,
amount,
fees,
);
return { result };
};Backend: from “Deposit events only” to real pay-with-crypto verification
On the backend we already had a generic entrypoint:
pub async fn verify_crypto_transaction(
asset: &BlockchainAsset,
deposit_input: Option<DepositInput>,
sender: &str,
amount: u128,
) -> Result<Option<String>> {
match asset {
BlockchainAsset::EVM { chain_id, token_address } => {
verify_evm_deposit(
*chain_id,
token_address.clone(),
deposit_input,
sender,
amount,
).await
}
BlockchainAsset::ICP { ledger_principal } => {
is_icp_token_supported(ledger_principal)?;
Ok(None)
}
BlockchainAsset::Bitcoin { rune_id } => {
verify_bitcoin_deposit(rune_id.clone(), deposit_input, amount).await
}
BlockchainAsset::Solana { spl_token } => {
verify_solana_deposit(spl_token.clone(), deposit_input, amount).await
}
}
}This worked well for deposits into our vault contracts, where the EVM path assumes the tx emits a Deposit event:
let log_event = get_valid_log_event(&chain_id, &tx_hash).await?;
// ...
match log_event {
LogEvent::Deposit(deposit_event) => { /* checks */ }
}For pay-with-crypto, this is wrong:
- the tx goes from onramper wallet → offramper wallet
- no vault contract is involved
- therefore, no
Depositlog is emitted
That gave us BlockchainError: EvmLogError - Not a Deposit event.
New EVM verification: regular transfers, not vault deposits
We refactored the EVM verification to support both cases:
- Vault deposits (existing flow) still parse a custom
Depositevent. - Pay-with-crypto flows inspect the transaction receipt and:
- for native payments: check
from,to, andvalue - for ERC-20: check a
Transferlog’sfrom,to,valueand token contract address.
- for native payments: check
At a high level:
pub async fn verify_evm_deposit(
chain_id: u64,
token_address: Option<String>,
deposit_input: Option<DepositInput>,
sender: &str,
amount: u128,
) -> Result<Option<String>> {
chains::chain_is_supported(chain_id)?;
if let Some(token) = token_address.clone() {
token::evm_token_is_approved(chain_id, &token)?;
};
let evm_input = match deposit_input {
Some(DepositInput::Evm(v)) => v,
_ => Err(OrderError::InvalidInput("Missing evm order input".into()))?,
};
let tx_hash = evm_input.tx_hash.clone();
// 1) Pull full receipt
let status = transaction::check_transaction_status(&tx_hash, chain_id).await;
let receipt = match status {
TransactionStatus::Confirmed(r) => Ok(r),
_ => Err(BlockchainError::EmptyTransactionHash),
}?;
// 2) Decide verification mode: vault Deposit event vs wallet Transfer
if let Some(contract_addr) = &receipt.contractAddress {
// vault deposit path (old logic)
let log_event = get_valid_log_event(&chain_id, &tx_hash).await?;
if let LogEvent::Deposit(deposit_event) = log_event {
// same checks as before (user, amount, token, expiry)
// ...
} else {
return Err(BlockchainError::EvmLogError("Not a Deposit event".into()).into());
}
} else {
// pay-with-crypto path: wallet → wallet transfer
verify_evm_wallet_payment(
chain_id,
token_address,
sender,
amount,
&receipt,
).await?;
}
Ok(Some(tx_hash))
}Where the payment path looks like:
async fn verify_evm_wallet_payment(
chain_id: u64,
token_address: Option<String>,
sender: &str,
amount: u128,
receipt: &TransactionReceipt,
) -> Result<()> {
// for ERC-20 we expect a Transfer log
if let Some(token) = token_address {
let transfer_log = event::parse_erc20_transfer(&receipt.logs)
.map_err(|_| BlockchainError::EvmLogError("No Transfer log".into()))?;
if transfer_log.from.to_lowercase() != sender.to_lowercase() {
return Err(BlockchainError::EvmLogError("Invalid sender".into()).into());
}
if transfer_log.value != amount {
return Err(BlockchainError::EvmLogError("Invalid amount".into()).into());
}
if transfer_log.token.to_lowercase() != token.to_lowercase() {
return Err(BlockchainError::EvmLogError("Invalid token".into()).into());
}
} else {
// native transfer (no token_address)
if receipt.from.to_lowercase() != sender.to_lowercase() {
return Err(BlockchainError::EvmLogError("Invalid sender".into()).into());
}
// here we fetch the tx value (we keep it abstract in this summary)
let value = transaction::get_transaction_value(&receipt.transactionHash, chain_id).await?;
if value != amount {
return Err(BlockchainError::EvmLogError("Invalid amount".into()).into());
}
}
Ok(())
}Important details:
senderis the onramper wallet in the pay-with-crypto path (for create-order deposits it remains the offramper).amountis the amount in smallest units we computed on the frontend from (price + offramper_fee) using the provider token decimals.- We still mark tx hashes as “spent” in the same
spent_transactionsmap, so the same tx cannot pay multiple orders.
Completing the order and appending a Fill
Once verification succeeds we mark the order as paid and append a fill:
if let Some(tx_hash) = tx_opt.clone() {
orders::set_payment_id(order.base.id, tx_hash.clone())?;
management::order::mark_order_as_paid(order.base.id)?;
// append fill with payment_id = tx_hash
let total = order.base.crypto.amount.max(1);
let locked = order.lock_amount;
let fee_part: u128 = (order.base.crypto.fee.saturating_mul(locked)) / total;
append_fill_if_new(
order.base.id,
FillRecord {
payer_user_id: order.onramper.user_id,
payer: order.onramper.address.clone(),
provider: order.onramper.provider.clone(),
fiat: order.price,
offramper_fee: order.offramper_fee,
crypto_amount: locked,
crypto_fee: fee_part,
payment_id: tx_hash.clone(),
tx_id: None,
created_at: ic_cdk::api::time(),
},
)?;
spent_transactions::mark_tx_hash_as_processed(tx_hash);
}This ties together:
- the fiat side (
price,offramper_fee) - the crypto side (
crypto_amount,crypto_fee`) - the payment id (
payment_id= hash / signature used as proof of payment)
Inspecting the fills
Once the payment and release paths complete, the order shows up as filled in the frontend:
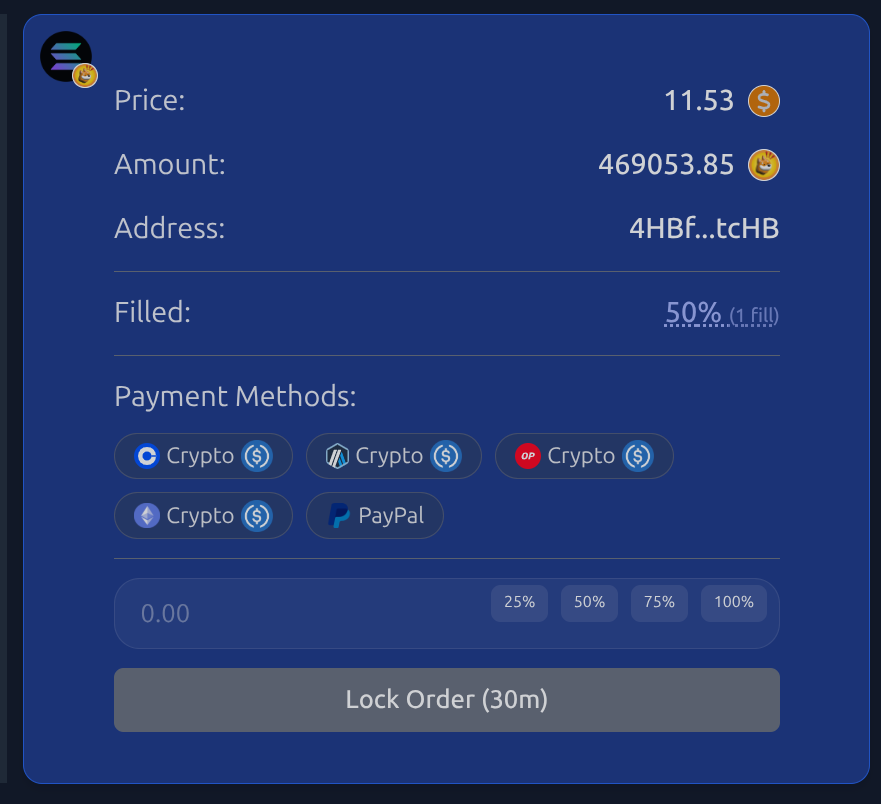
And we can drill into the list of fills for a given order:
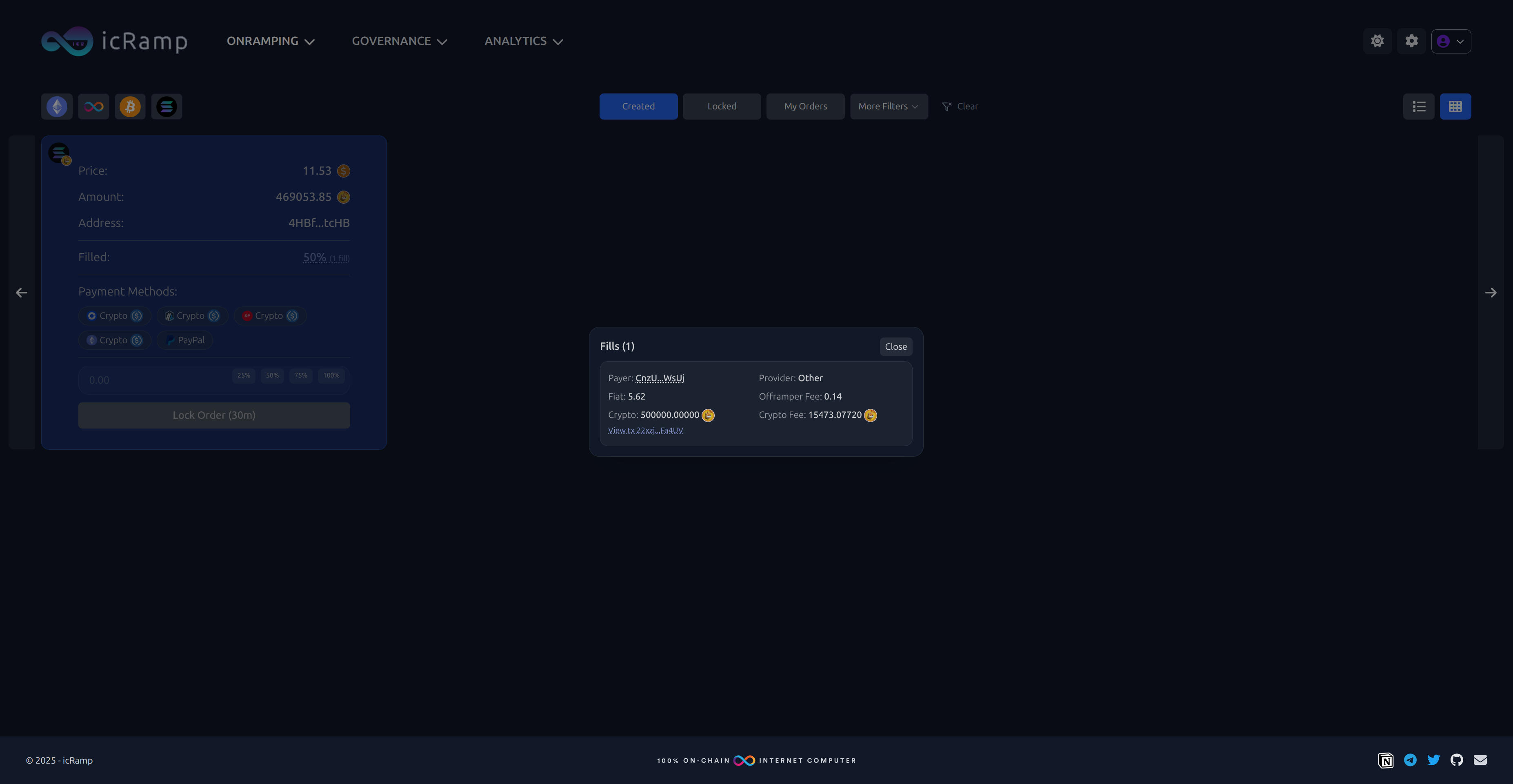
Wrap-up & what’s next
This devlog closes the loop started in #19:
- Users can register Crypto providers (EVM/SOL/ICP).
- Onramper selects a provider when locking an order.
- The order card shows a chain-aware Pay with Crypto button based on the provider asset.
- We compute (
price + offramper_fee) in smallest token units using the provider tokendecimals. - We send funds from onramper wallet → offramper wallet, not via the vault.
- The backend verifies those payments chain-specifically (EVM/Solana/Bitcoin/ICP), and appends a fill with the correct payment id.
The core bridge is now trustless, multi-chain, and fully instrumented – which is exactly where we wanted the “pay with crypto” feature to land.
This, together with all the features implemented in previous devlogs, almost wraps up the entirety of the milestone.
In the next and last devlog we will wrap up by simplifying the EVM smart contracts and getting rid of the onchain's evm vault for commit and uncommit, and introduce the usage of ic_alloy for simpler evm operations.
With that, we will finally record the milestone video and present the end of the grant that supported these #20 devlogs!
Stay Updated
Get notified when I publish new articles about Web3 development, hackathon experiences, and cryptography insights.
You might also like

icRamp Devlog #19 — Pay with Crypto (Frontend UX & Provider Flows)
Frontend wiring for the experimental 'pay with crypto' path: crypto providers in the user profile, filtered provider selection in Create Order, and a compact order card UX for onrampers choosing how to pay.

icRamp Devlog #18 — Pay with Crypto (Experimental Trustless P2P Bridge)
We add an experimental 'pay with crypto' path that lets onrampers settle in stables on a different chain than the escrowed asset. Includes provider model refactor and order validation. Frontend exposure starts with stables for speed.

icRamp Devlog #17 — Liquid Orders: Partial Fills
We add partial fills: the onramper can lock only a fraction of the order, pay, and get a proportional crypto payout while the rest stays open. Single lock path, pro-rata fees, idempotent fill records, and listener-safe completion.